Download and print as a PDF (190kB pdf)
On this page
This leaflet is intended to answer some of the questions of patients or carers of patients diagnosed with convergence insufficiency under the care of University Hospitals Sussex NHS Foundation Trust.
What is Convergence Insufficiency (CI)?
Convergence insufficiency is a condition where a person is unable to converge their eyes effectively; i.e. move both eyes towards the nose at the same time. Convergence is needed to keep both eyes focussed on near objects; e.g. reading a book. If convergence insufficiency causes symptoms it can be treated with exercises.
What symptoms does CI cause?
Typical symptoms include:
• Headaches (front of head / around eyes).
• Eye strain.
• Blurred or double vision for near work.
• Difficulty changing focus from distance to near.
What treatment is available?
CI can usually be treated with exercises but the treatment will only work if the exercises are carried out regularly.
Pen Convergence
• Hold a target (e.g. pen) at arm’s length then slowly and smoothly bring the target towards your nose.
• Once the target appears double, hold it at that point and try to make it single again by blinking and focussing your eyes as much as possible.
• If you are able to maintain a single image at this point, continue with the exercise.
• If unable to maintain a single image, take the target back a little until it is single then try again.
• The aim is to try and get the target as close as possible to your nose.
Jump Convergence
• Bring a target (e.g. pen) as close as possible to your nose keeping it clear and single and stop before it becomes double.
• Then look at an object in the distance for a few seconds and then look back towards the pen keeping it clear and single.
• Look at the far object again and bring the pen a little closer and then look back at the pen trying to maintain a clear and single image.
• The aim is to try and get the target as close as possible to your nose.
Dot Card
• The dot card is held up to the tip of your nose and you look at the dot which is
furthest away.
• If this dot is clear and single then look to the next dot towards you.
• As you look at each nearer dot you need to try and ensure this dot is clear and
single.
• If you are unable to get the dot you are focussing on single, go back to the previous dot and try again.
• You will notice the dots in front of, or behind, the dot you are focussed on will appear double, this is normal and you should be able to see the below shapes as you focus on the dots:
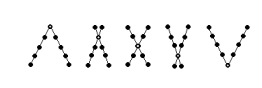
Will I strain my eyes by doing the exercises?
It is very important to relax your eyes after each exercise by looking into the distance or by closing your eyes for a few minutes. The eyes may feel uncomfortable after the exercises, which is to be expected but too much exercising and / or not enough relaxation may make the eyes feel even more uncomfortable.
Exercises prescribed:
Space to write the exercise prescribed.
How often to perform them:
Space to write how often to perform the exercises.
Orthoptist’s name:
Space to write your Orthoptist’s name.
The exercises are only effective when carried out frequently. Please follow the directions given by your Orthoptist.
Contact Details
St Richard’s Hospital
St Richard’s Hospital
Spitalfield Lane
Chichester
West Sussex
PO19 6SE
Orthoptist
01243 831499
Southlands Hospital
Southlands Hospital
Upper Shoreham Road
Shoreham-by-Sea
West Sussex
BN43 6TQ
Orthoptist
01273 446077
The information here is for guidance purposes only and is in no way intended to replace professional clinical advice by a qualified practitioner.