Download and print as a PDF (403kB pdf)
On this page
- What is this information about?
- Why have I been given this information?
- Why have you given me a boot rather than a plaster cast?
- Will my boot be the right size for me?
- How do I put my boot on and take it off?
- Can I wear a boot if I have diabetes or peripheral neuropathy (loss of feeling in your foot)?
- How can I contact the Plaster Room?
- What do I need to know about wearing other footwear and walking while I have my boot?
- Other questions that people often ask us (FAQS):
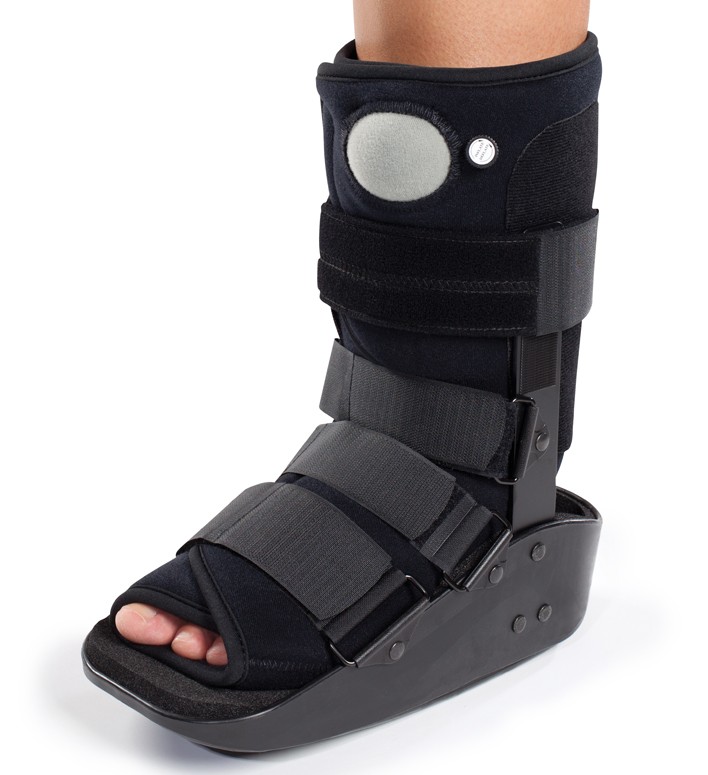
* Be aware, your boot may be slightly different to the pictures
What is this information about?
This information is about the special boot that you have been given to keep you comfortable while your foot, ankle or leg injury heals. It tells you:
- why you have been given a boot
- how to put your boot on and take it off
- the answers to some other questions that people who wear a boot often ask (FAQs)
Why have I been given this information?
You have been given this information because we have given you a special boot to wear after your injury. The advice in this information, if you follow it, will help you to wear your boot in the right way and keep you as comfortable as possible.
Why have you given me a boot rather than a plaster cast?
You have been given a boot as you have a stable injury or fracture. This means that your broken bones are unlikely to move around.
When you have a stable injury, you do not need a plaster cast to hold the part of your body that is injured in place.
Although you do not need to wear a cast, wearing a boot can help because it lets you put your weight on to your injured foot.
You can remove your boot so that you can move your ankle. This helps to keep your blood circulating well and so can help to heal your injury.
Many people with a stable foot injury find that it is easier to manage with their injury if they wear a boot.
Will my boot be the right size for me?
We have three sizes of boot and will give you the best fit for you. Your boot should fit so that your toes do not hang over the edge.
How do I put my boot on and take it off?
To take the boot off:
- Open the Velcro straps and fold them back on themselves.
- Open the foam inner and slide your foot out:

To put the boot on:
- open the front of the boot
- slide your foot in and make sure your heel is as far back as possible
- do the straps up one by one
The boot should be snug not tight.
Can I wear a boot if I have diabetes or peripheral neuropathy (loss of feeling in your foot)?
Yes, but you must take extra care of your feet.
- If you know you have peripheral neuropathy, or you think you have loss of feeling in your foot for any other reason, do tell your A&E clinician.
- If you have diabetes do check your feet often for any red areas that that do not go away. This may look different in black or brown skin. In these, the colour of the area may look different from the surrounding skin. Do let the A&E department or the Plaster Room staff know if you find any.
How can I contact the Plaster Room?
Plaster rooms
Worthing Hospital
01903 205 111
Ext. 85445
St. Richard’s Hospital
01243 788 122
Ext. 33393
What do I need to know about wearing other footwear and walking while I have my boot?
- Try to use a shoe of similar height to the boot on your other foot. This will help you walk more easily.
- Do not wear completely flat shoes such as flip-flops.
Other questions that people often ask us (FAQS):
Can I take the boot off?
Yes. You only need to wear the boot when you are walking.
Must I wear the boot when I am sleeping?
No. You do not need to wear the boot while you are sleeping.
You may wear the boot while you are sleeping for the first week after your injury if you find it more comfortable.
Can I drive with the boot on?
No.
What do I do if the boot breaks?
Contact the Plaster Room.
Who should I contact if I need further information about my boot after I have read this information?
Please contact the Plaster Room.
This information is intended for patients receiving care in Worthing and Chichester St.Richard’s Hospitals.
The information here is for guidance purposes only and is in no way intended to replace professional clinical advice by a qualified practitioner.